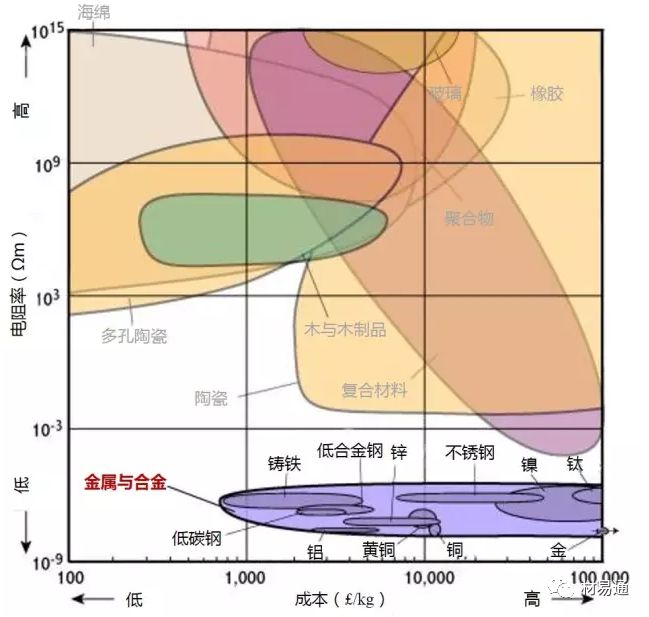
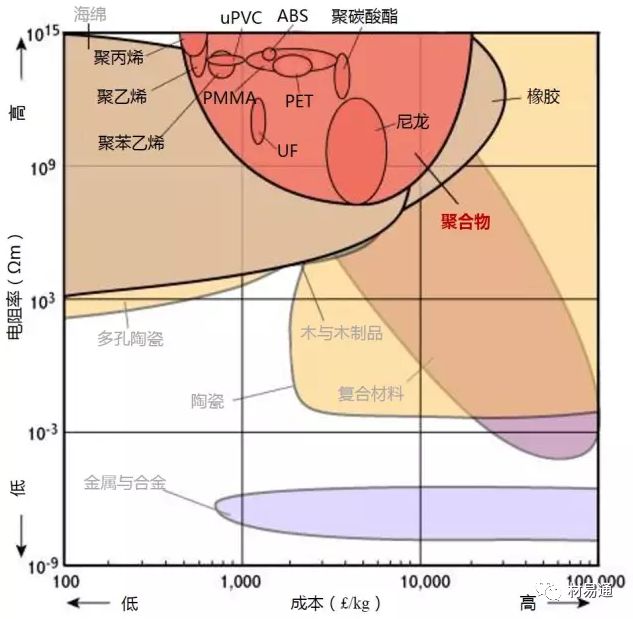
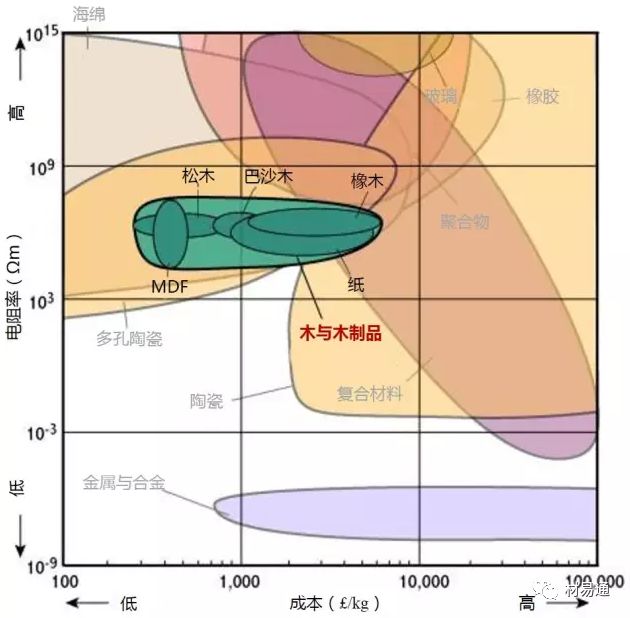
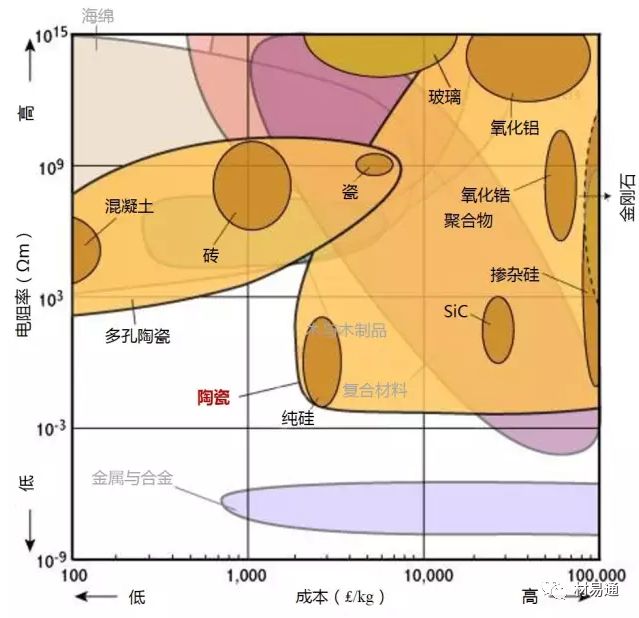
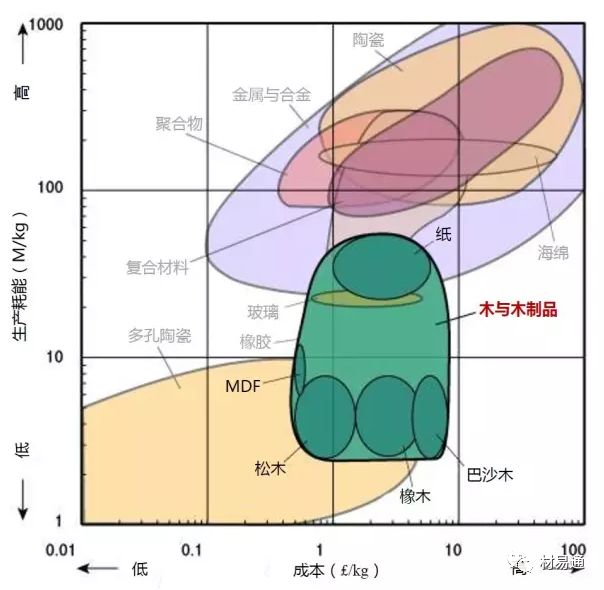
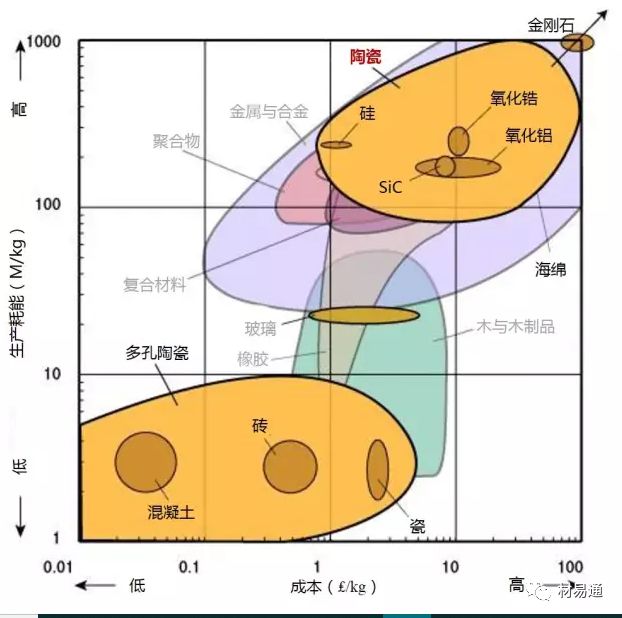
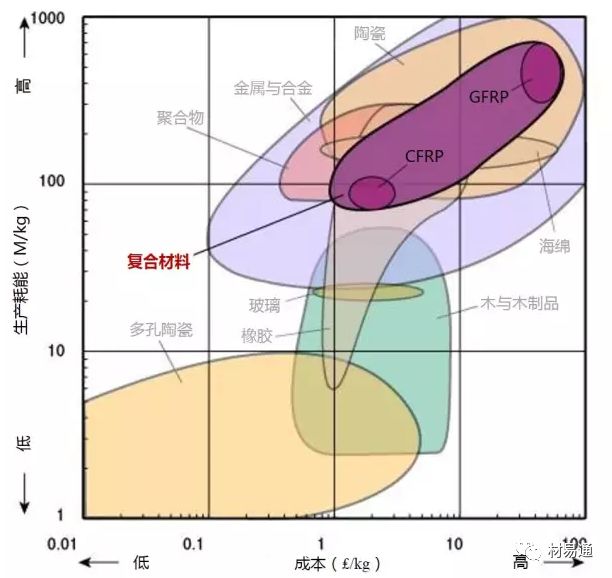
為了保證圖片的清晰度,本文保留了英文原圖,未對材料名稱進行編譯。讀者可先通過列表對相關(guān)材料的中英文名進行熟悉后,再瀏覽圖片。
(點擊圖片再放大,可更直觀查看圖片細節(jié))
1
材料性能對比圖中所涉及的材料
材料類別 | 英文名 | 中文名 |
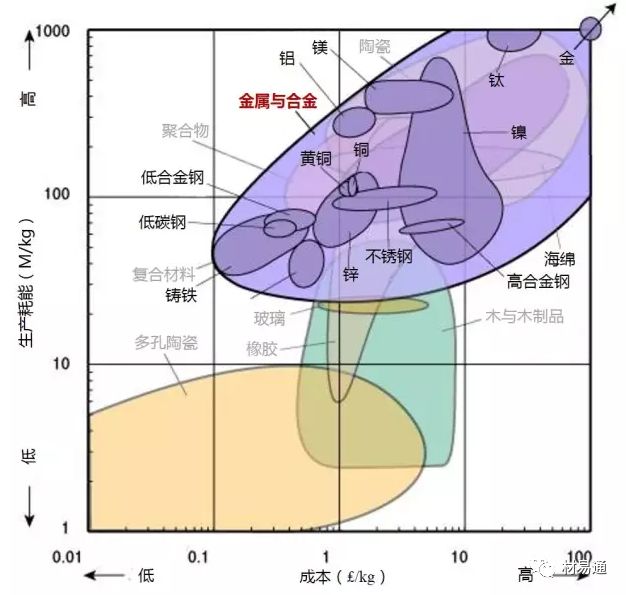
Metals 金屬及合金 | Al alloys | 鋁合金 |
Cu alloys | 銅合金 | |
Lead alloys | 鉛合金 | |
Mg alloys | 鎂合金 | |
Ni alloys | 鎳合金 | |
Steels | 鋼 | |
Stainless steels | 不銹鋼 | |
Tin alloys | 錫合金 | |
Ti alloys | 鈦合金 | |
W alloys | 鎢合金 | |
Pb alloys | 鉛合金 | |
Zn alloys | 鋅合金 | |
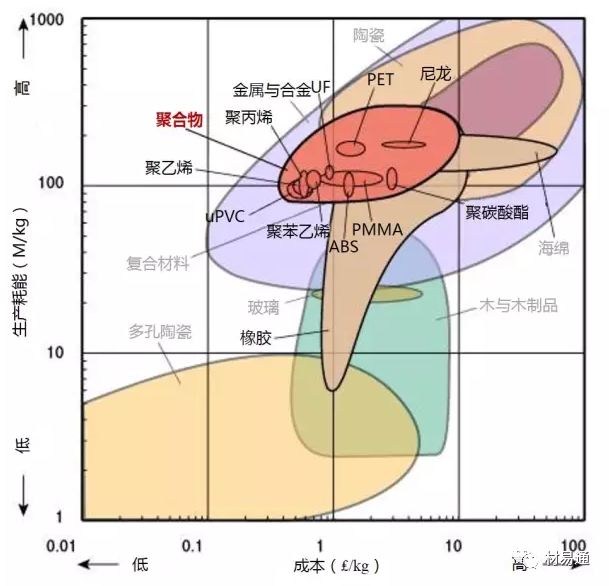
Polymers 聚合物 | ABS | ABS材料 |
CA | 醋酯纖維 | |
Ionomers | 離聚物 | |
Epoxy | 環(huán)氧樹脂 | |
Phenolics | 酚醛塑料 | |
PA | 聚酰胺 | |
PC | 聚碳酸酯 | |
Polyester | 聚酯纖維 | |
PEEK | 聚醚醚酮 | |
PE | 聚乙烯 | |
PET | 熱塑性聚酯 | |
PMMA | 有機玻璃 | |
POM | 聚甲醛樹脂 | |
PP | 聚丙烯 | |
PS | 聚苯乙烯 | |
PTFE | 聚四氟乙烯 | |
PVC | 聚氯乙烯 | |
Elastomers 橡膠 | Butyl rubber | 丁基橡膠 |
EVA | 乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物 | |
Isoprene | ||
Natural rubber | 天然橡膠 | |
Neoprene | 氯丁膠 | |
PU | 聚氨酯 | |
Silicones | 有機硅塑料 | |
Ceramics 陶瓷 | Al2O3 | 氧化鋁 |
AlN | 氮化鋁 | |
B4C | 碳化硼 | |
SiC | 碳化硅 | |
Si3N4 | 氮化硅 | |
WC | 碳化物 | |
Brick | 磚 | |
Concrete | 混凝土 | |
stone | 石頭 | |
Glasses 玻璃 | Soda-lime glass | 鈣鈉玻璃 |
Borosilicate | 硼硅玻璃 | |
Silica glass | 石英玻璃 | |
Glass ceramic | 玻璃陶瓷 | |
Composites 復(fù)合物 | CFRP | 碳纖維增強復(fù)合材料 |
GFRP | 玻璃纖維增強塑料 | |
Al-SiC | 碳化硅增強鋁基材料 | |
Foams 泡沫材料 | Flexible foams | 柔性聚合物泡沫 |
Rigid foams | 硬質(zhì)聚合物泡沫 | |
Natural materials 天然材料 | Cork | 軟木 |
Bamboo | 竹子 | |
Wood | 木頭 |
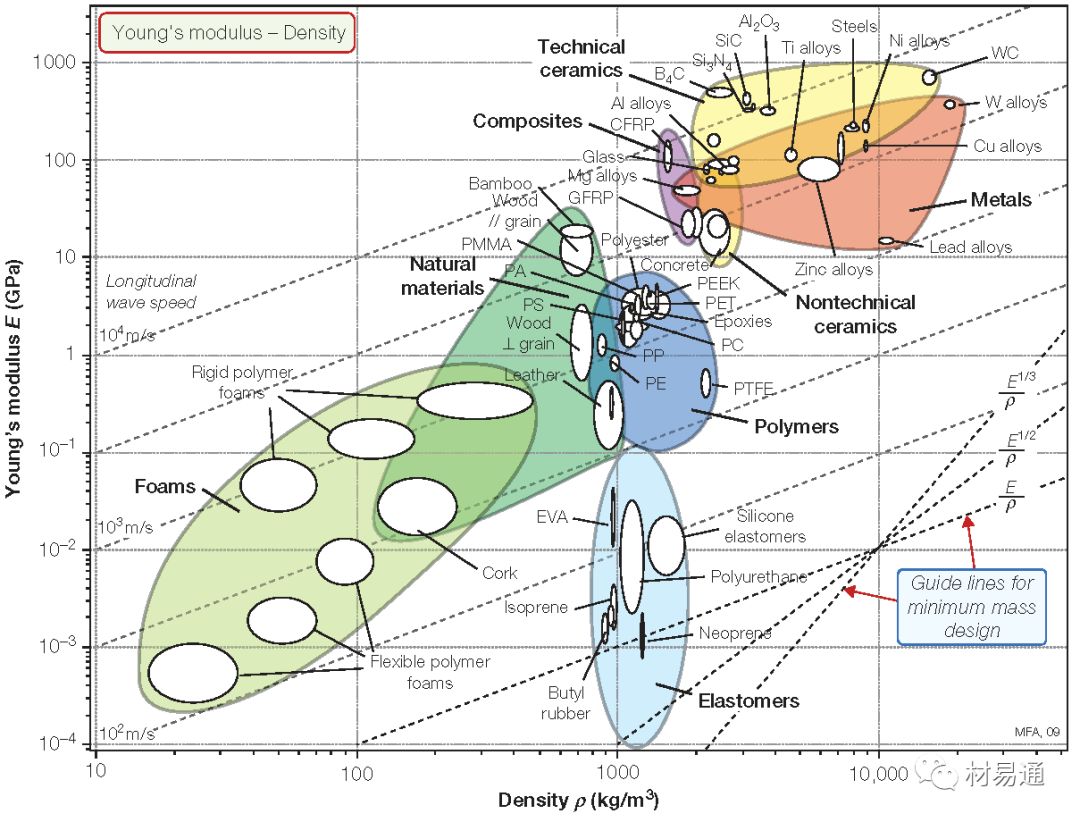
2
楊氏模量-密度
Young’s modulus vs. Density
3
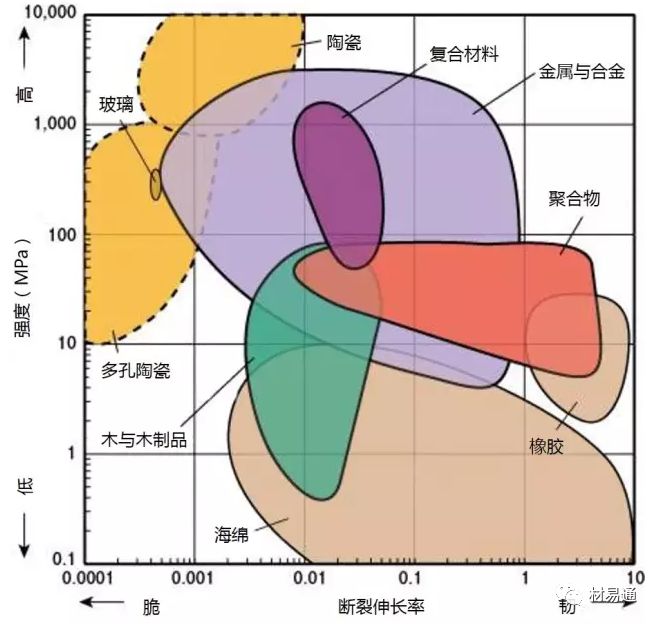
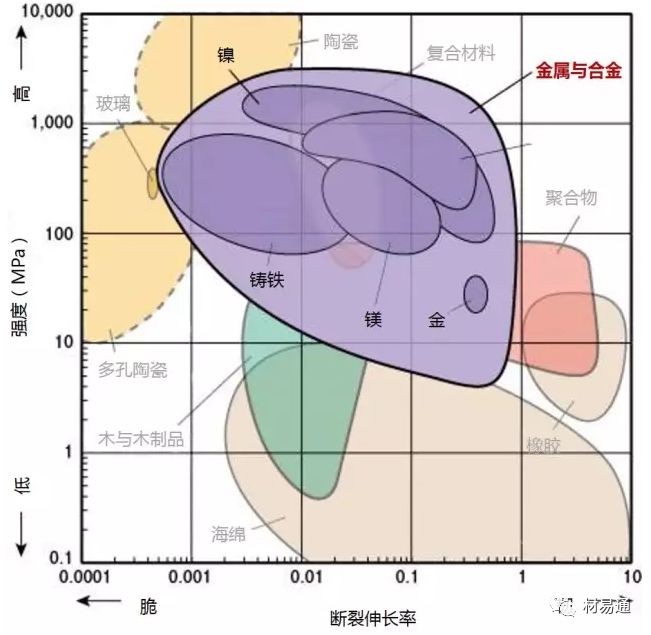
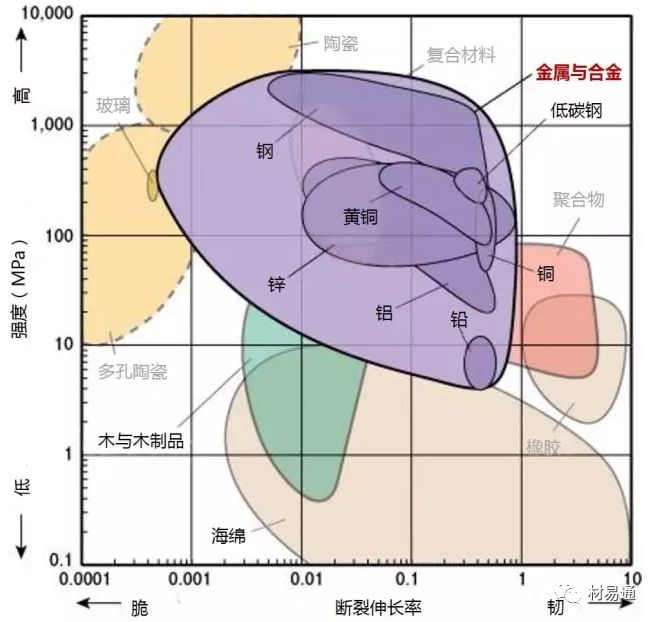
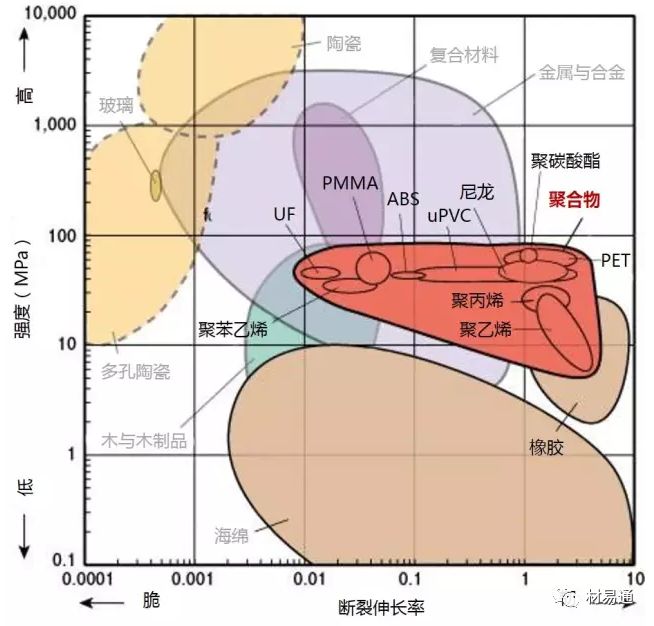
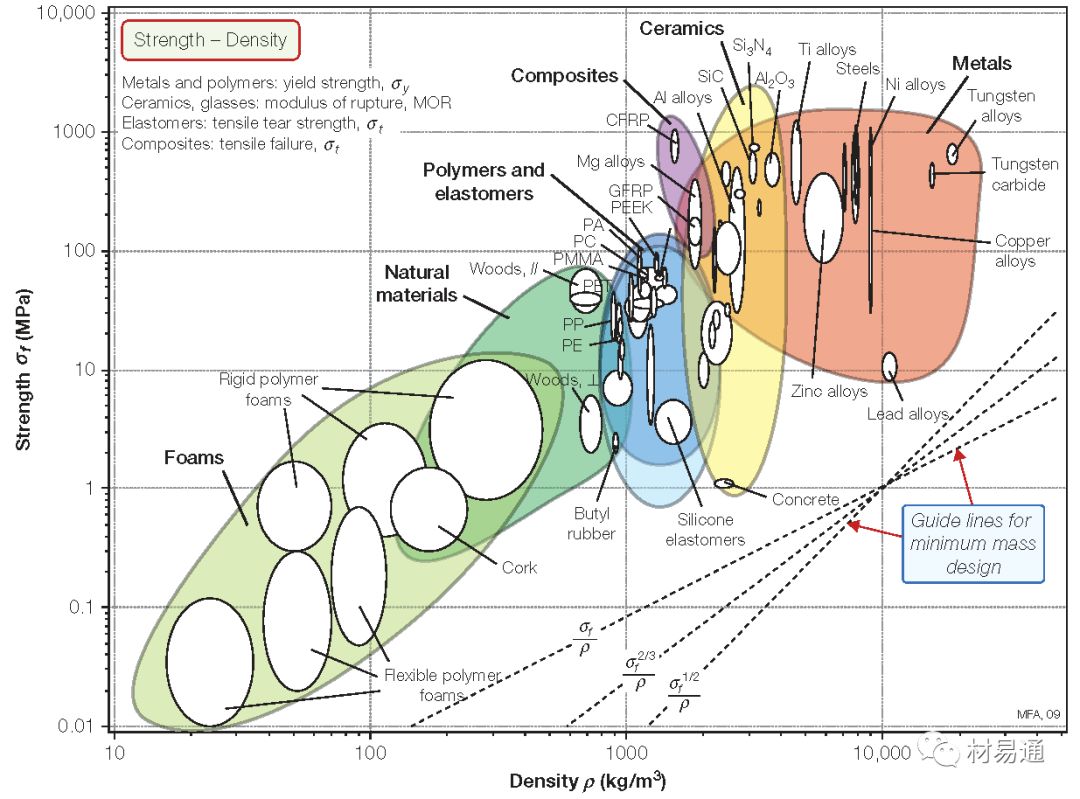
強度—密度
Strength vs. Density
4
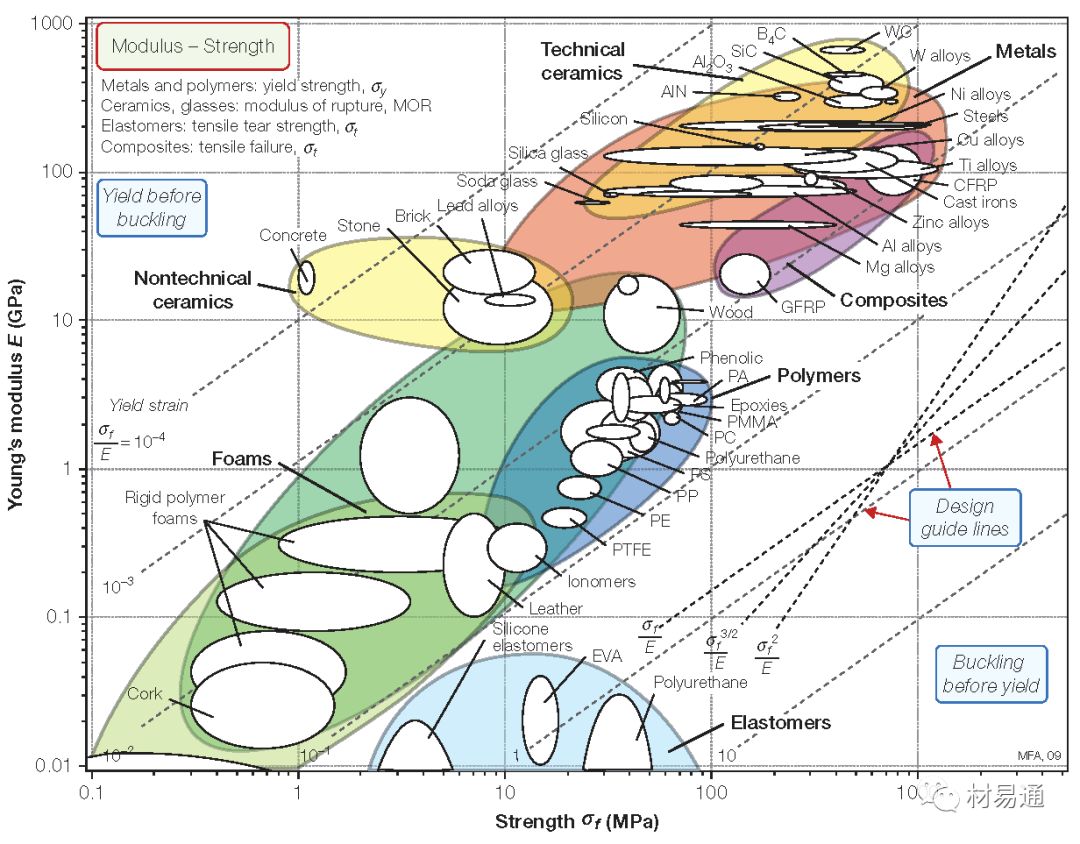
楊氏模量—強度
Young’s modulus vs. Strength
5
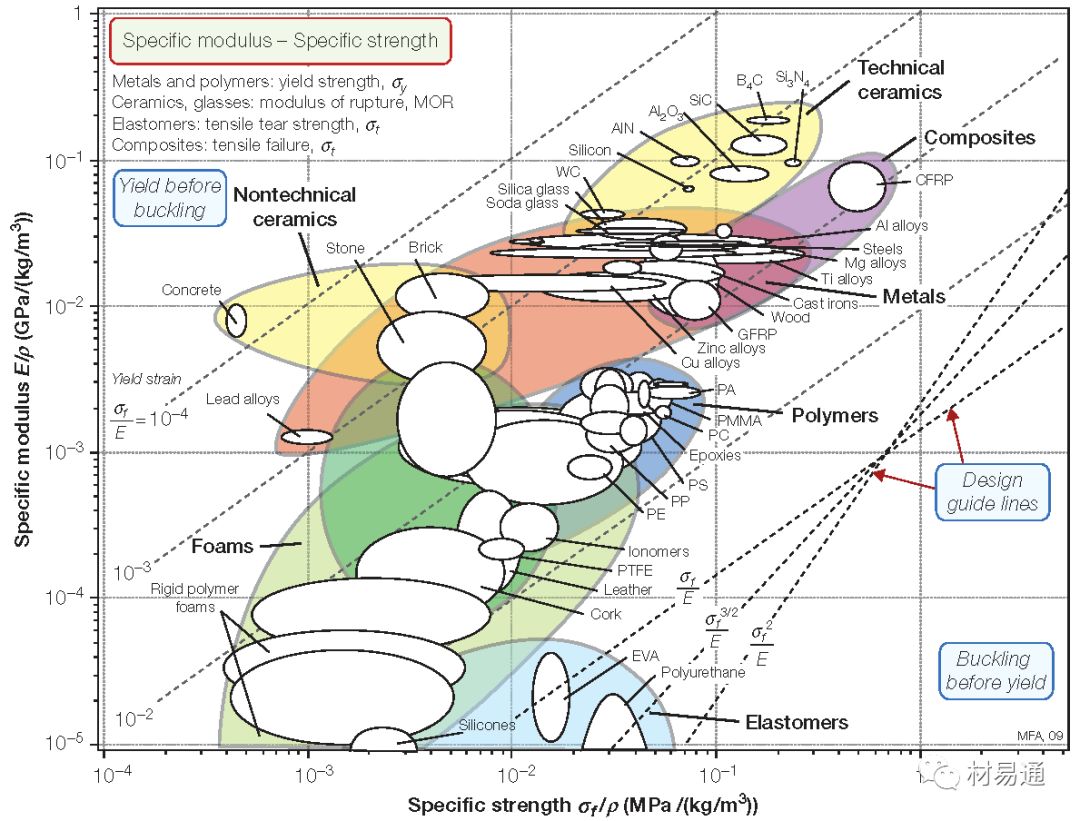
比模量—比強度
Specific modulus vs. Specific strength
比模量是單位密度的彈性模量,比模量是材料承載能力的一個重要指標,比模量越大,零件的剛性就愈大,也稱為“比剛度”。
比強度為材料的強度與材料表觀密度之比。比強度越高表明達到相應(yīng)強度所用的材料質(zhì)量越輕。優(yōu)質(zhì)的結(jié)構(gòu)材料應(yīng)具有較高的比強度,才能盡量以較小的截面滿足強度要求,同時可以大幅度減小結(jié)構(gòu)體本身的自重。
6
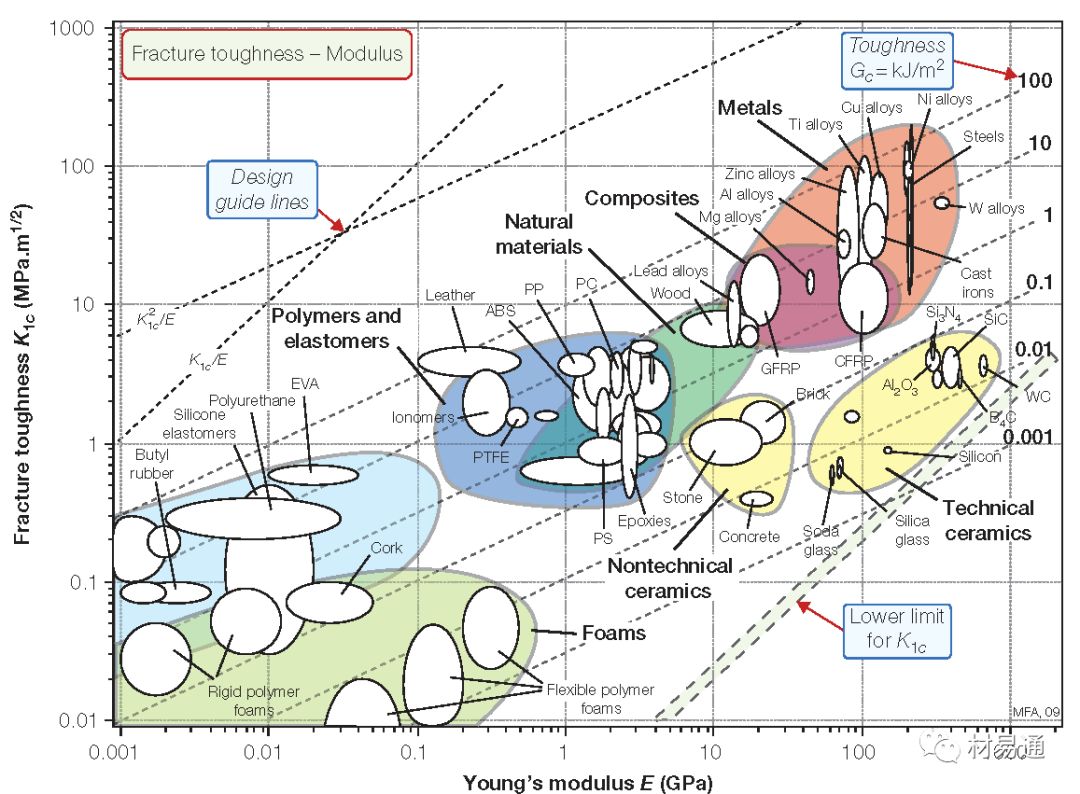
斷裂韌性與楊氏模量
Fracture toughness vs. Young’s modulus
7
斷裂韌性與強度
Fracture toughness vs. Strength

8
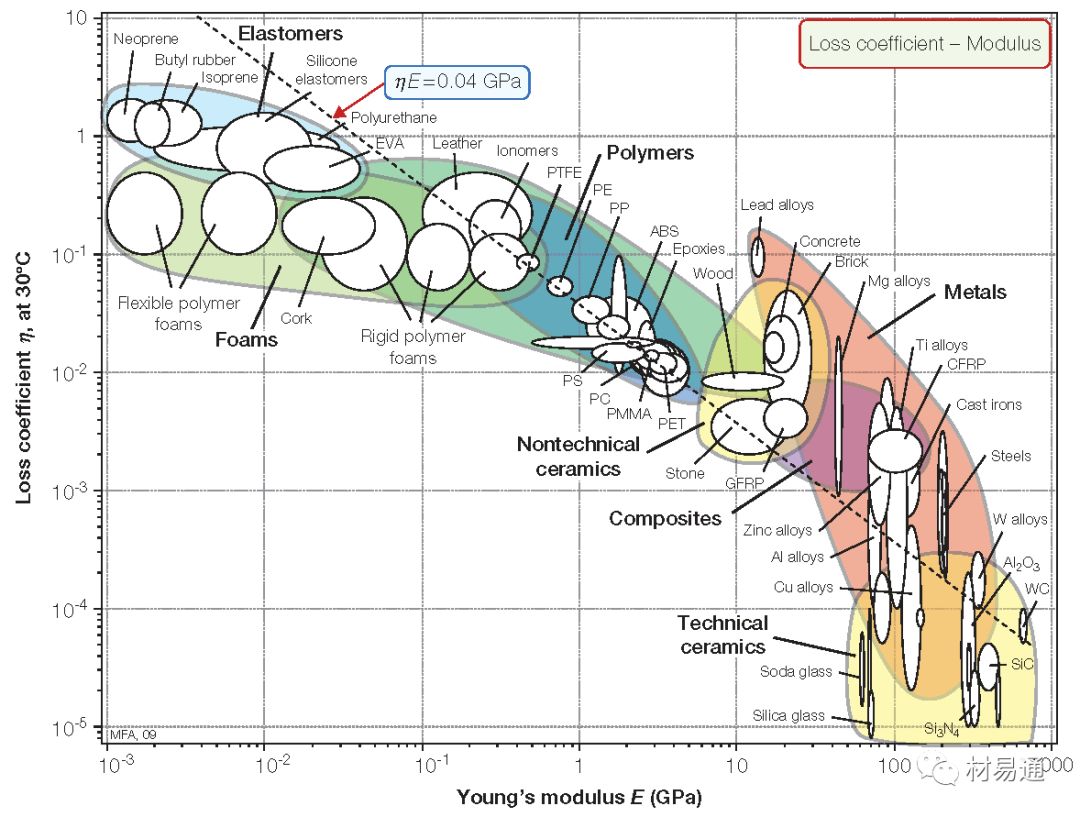
損耗因子與楊氏模量
Loss coefficient vs. Young’s modulus
9
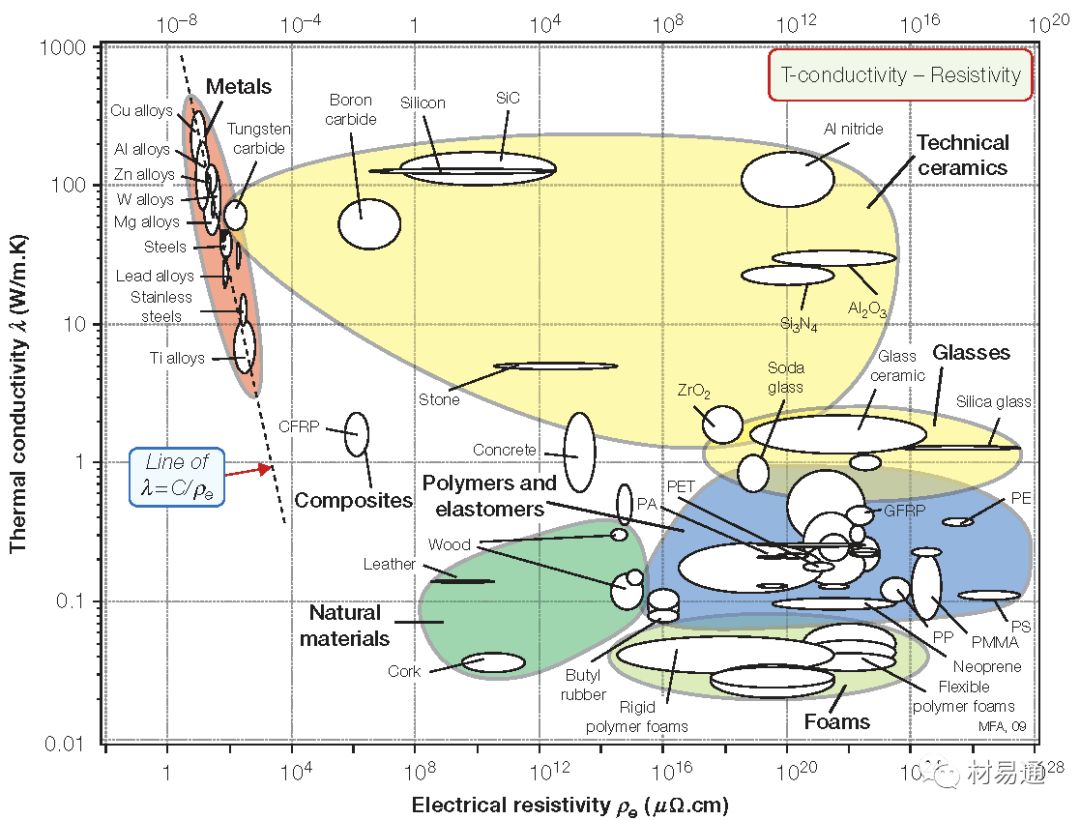
導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)與電阻率
Thermal conductivity vs. Electrical resistivity
導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)是指在穩(wěn)定傳熱條件下單位面積傳遞的熱量,導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)僅針對存在導(dǎo)熱的傳熱形式,當存在其他形式的熱傳遞形式時,如輻射、對流和傳質(zhì)等多種傳熱形式時的復(fù)合傳熱關(guān)系,該性質(zhì)通常被稱為表觀導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)、顯性導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)或有效導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)。
電阻率是指材料的電阻與橫截面積的乘積與長度的比值,是衡量材料導(dǎo)電性能的物理參數(shù)。電阻率不僅與材料種類有關(guān),而且還與溫度、壓力和磁場等外界因素有關(guān)。
10
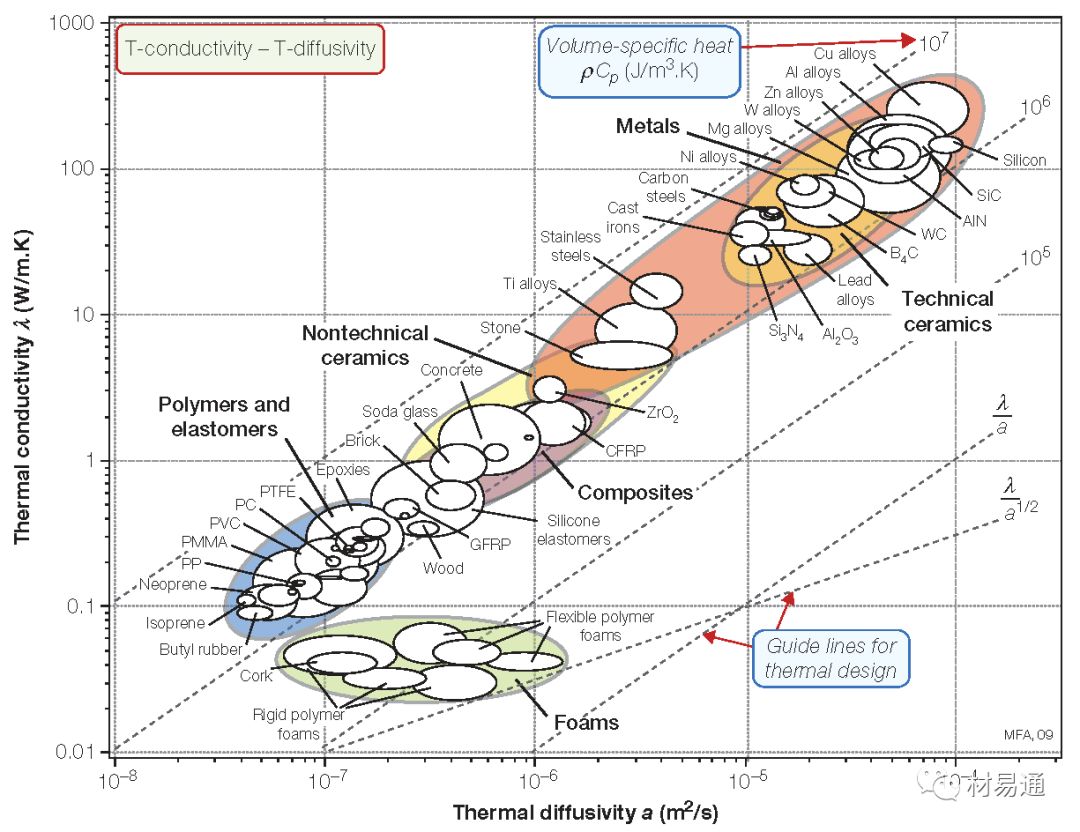
導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)與熱擴散系數(shù)
Thermal conductivity vs. Thermal diffusivity
11
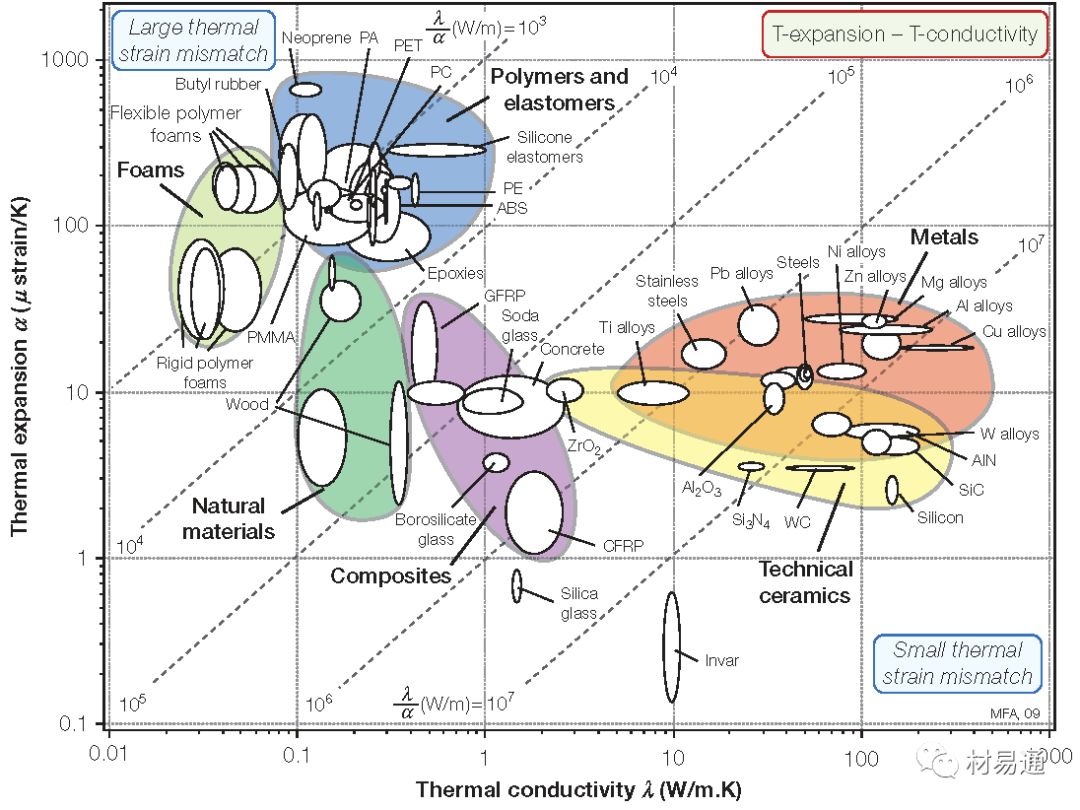
線膨脹系數(shù)—導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)
Thermal expansion vs. Thermal conductivity
12
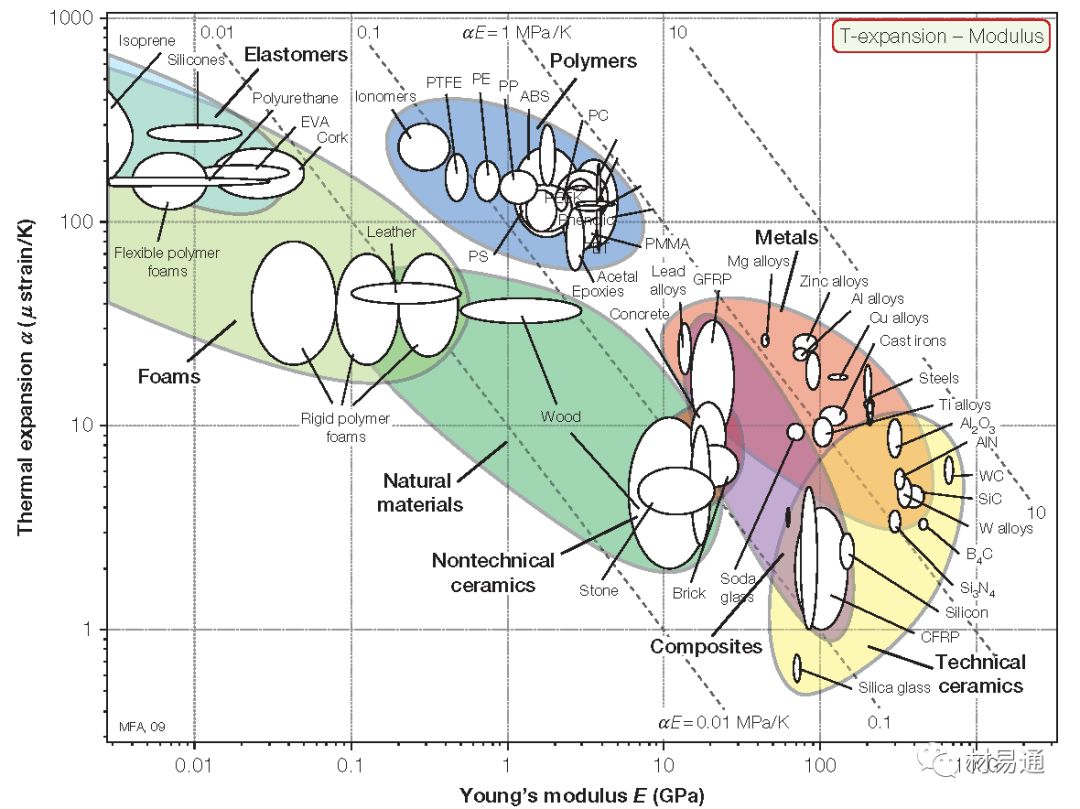
線膨脹系數(shù)—楊氏模量
Thermal expansion vs. Young’s modulus
13
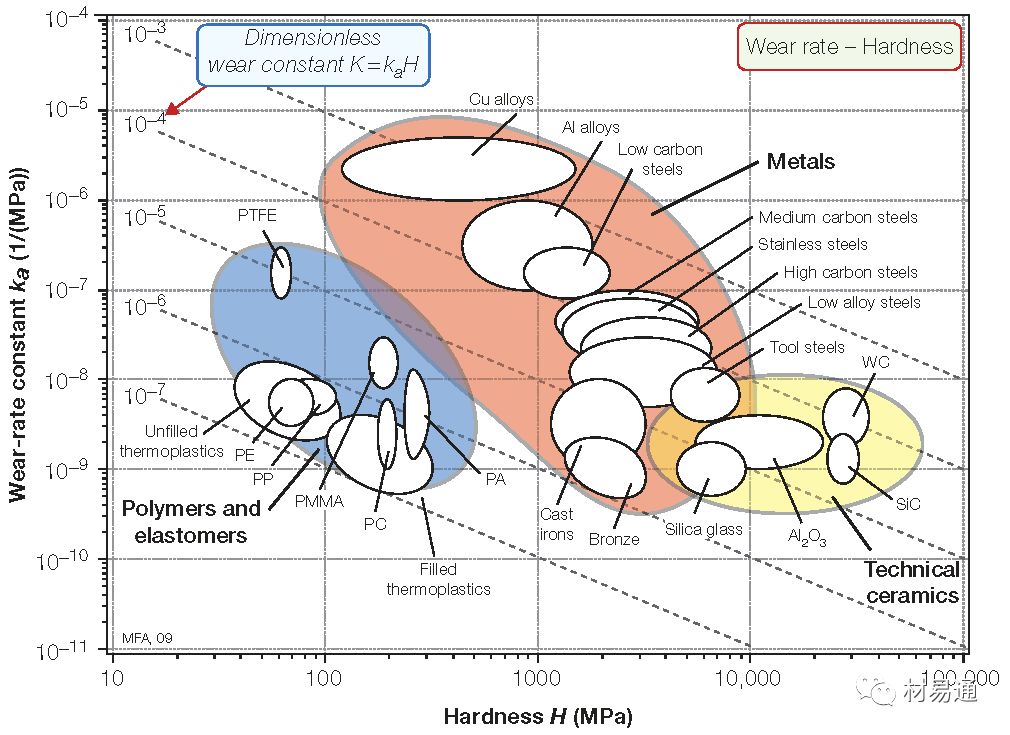
磨損常數(shù)與硬度
Wear rate constant vs. Hardness
磨損常數(shù)是指材料在一定壓力下的磨損量。
硬度是指材料局部抵抗硬物壓入其表面的能力。
一般情況下,材料抗疲勞磨損能力隨表面硬度的增加而增強,而表面硬度一旦越過一定值,則情況相反。
14
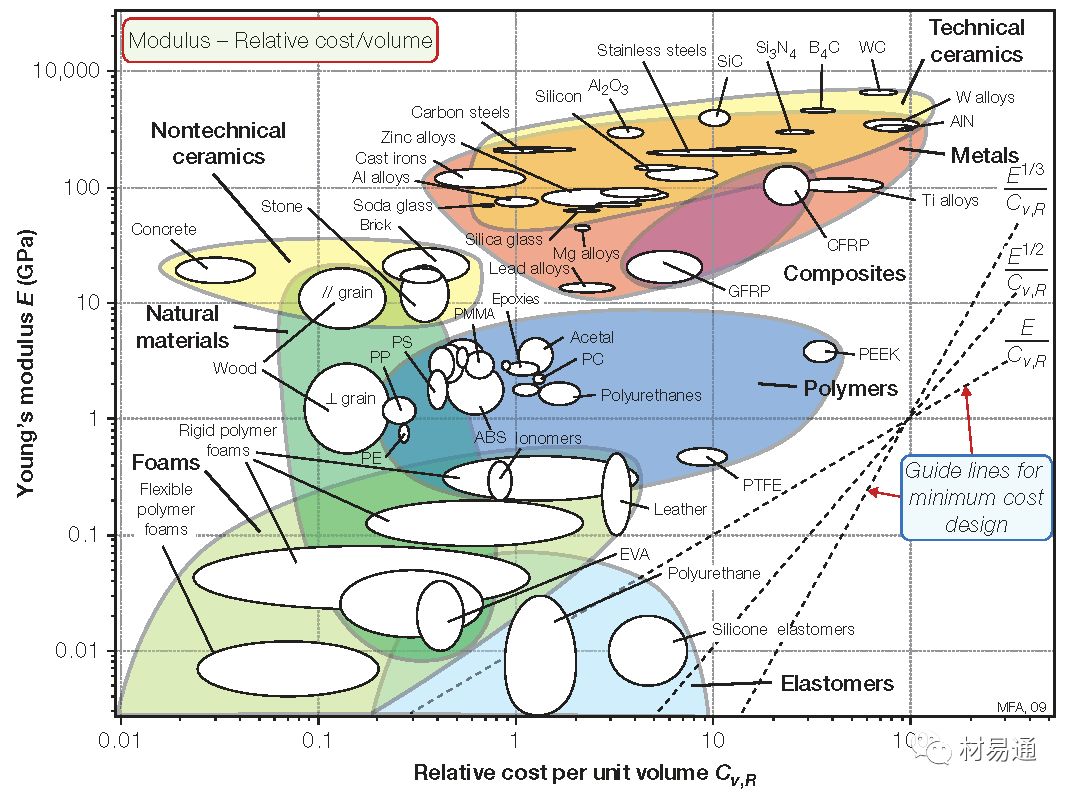
楊氏模量—相對成本
Young’s modulus vs. Relative cost per unit volume
15
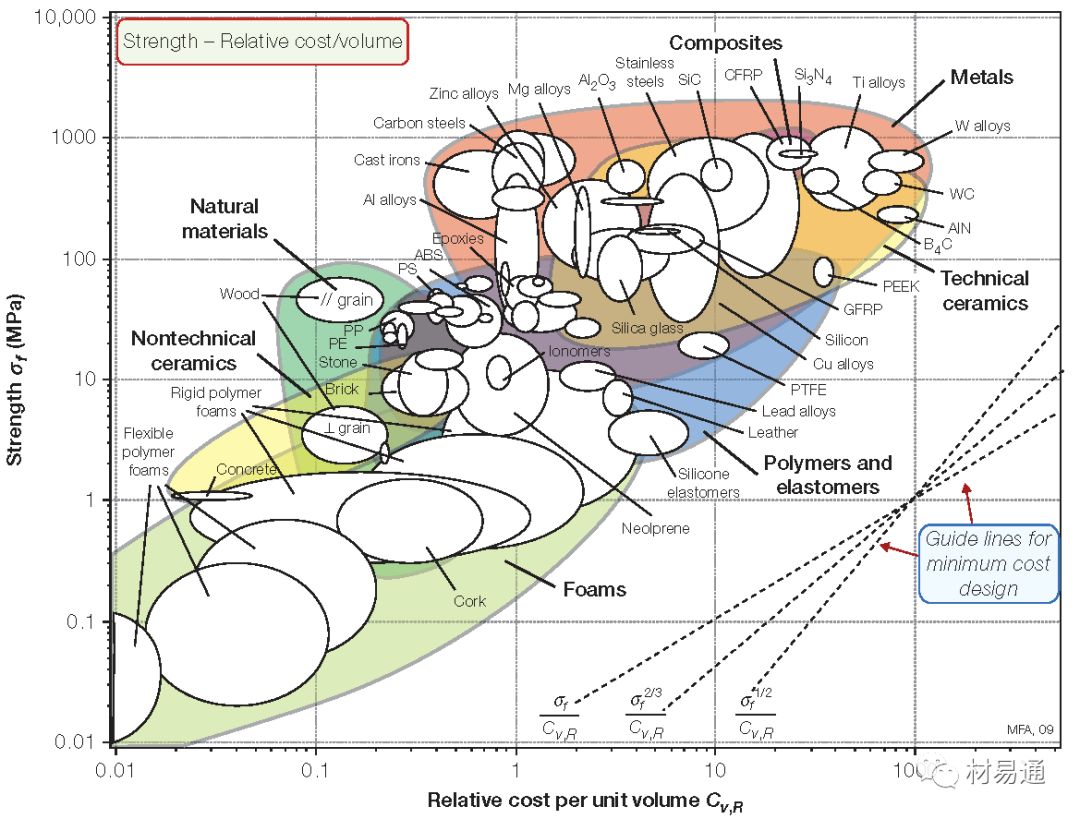
強度—相對成本
Strength vs. Relative cost per unit volume
16
導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)—強度
Thermal conductivity vs. Strength
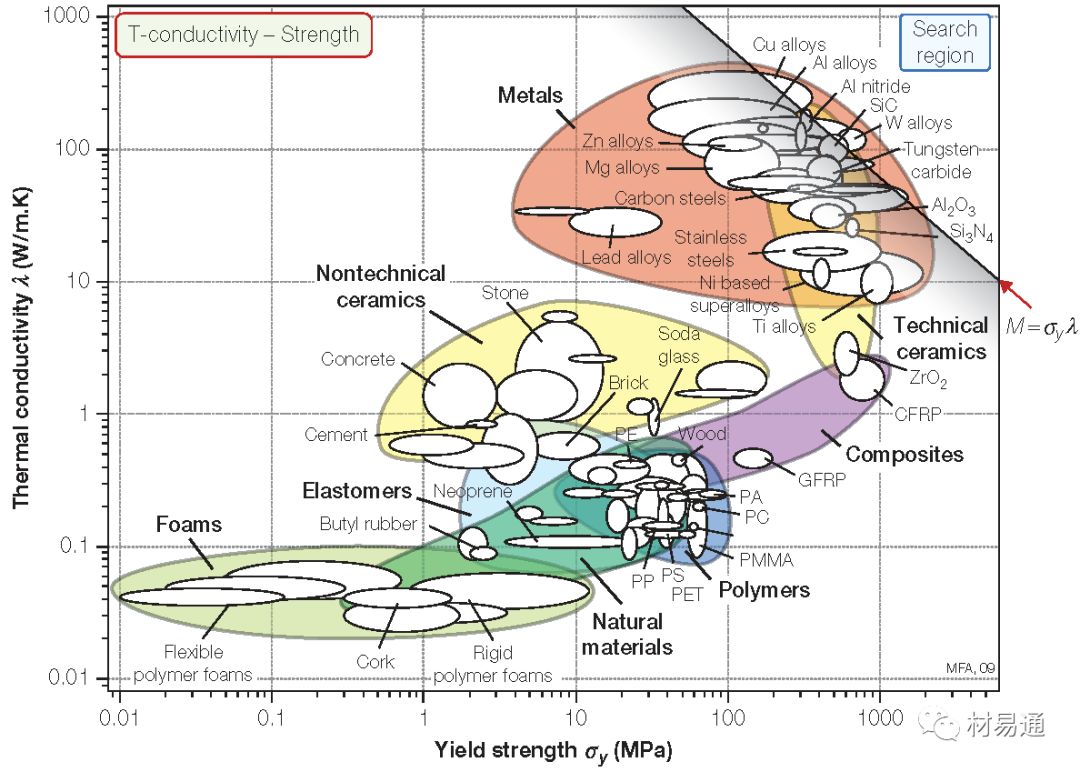
17
強度—介電損耗
Strength vs. Dielectric loss factor
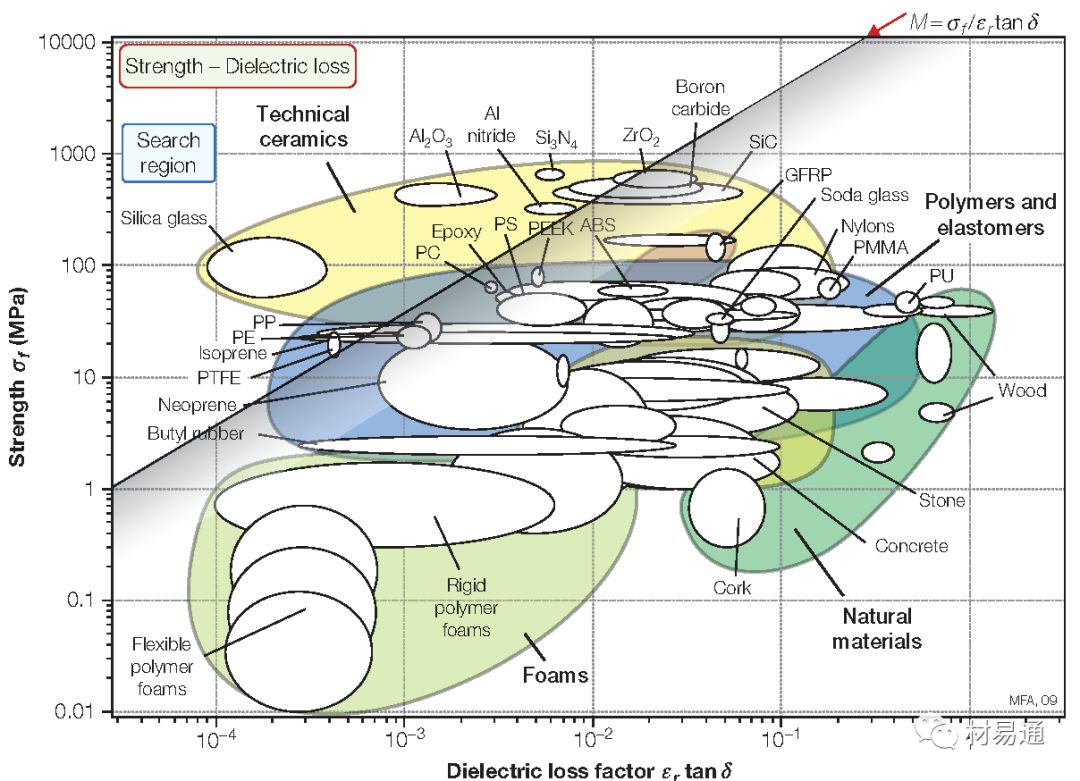
18
強度—介電損耗(聚合物)
Strength vs. Dielectric loss factor(Polymers)

19
強度—介電損耗(陶瓷)
Strength vs. Dielectric loss factor(Ceramics)
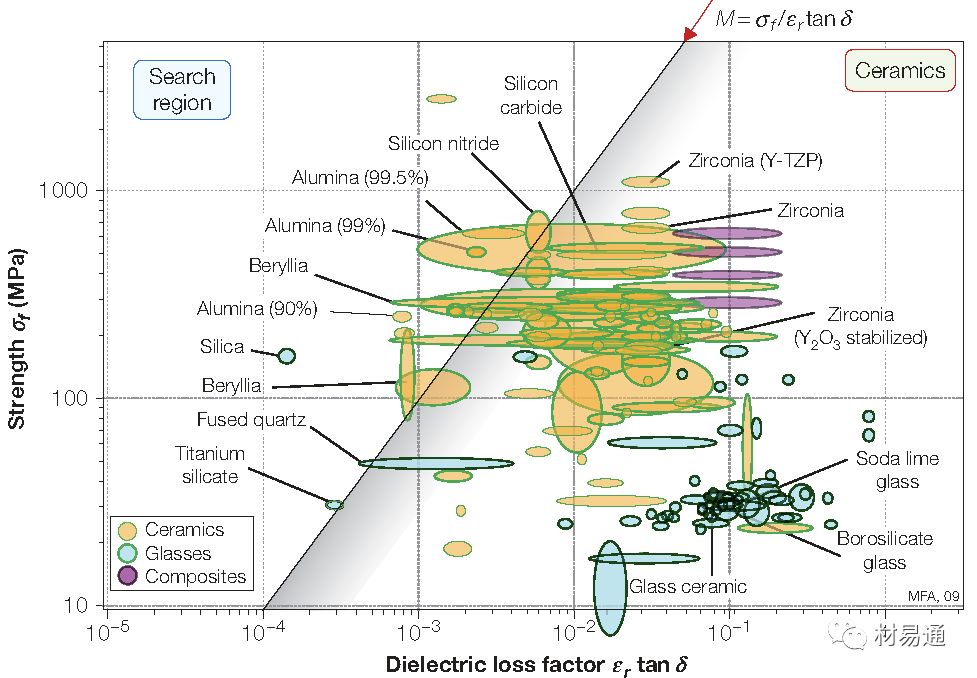
20
電阻率—楊氏模量
Electrical resistivity vs. Young’s modulus
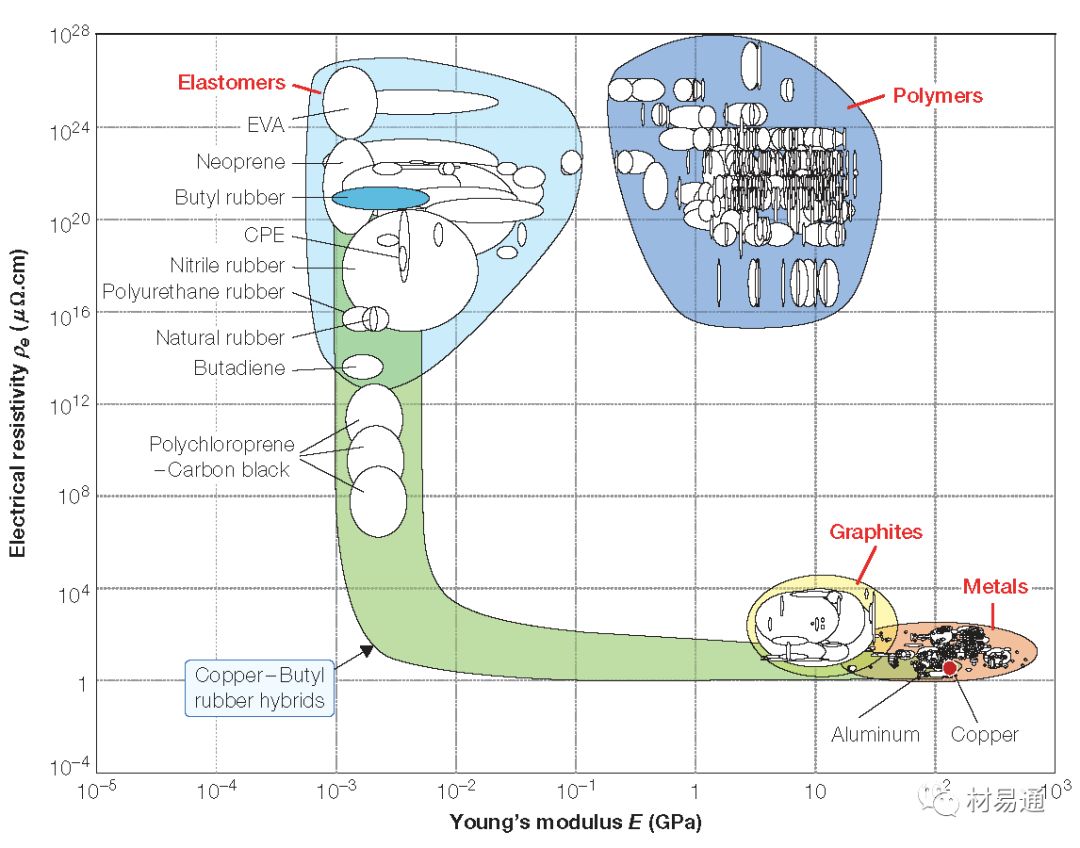
21
線膨脹系數(shù)—最高工作溫度
Thermal expansion vs. Maximum service temperature
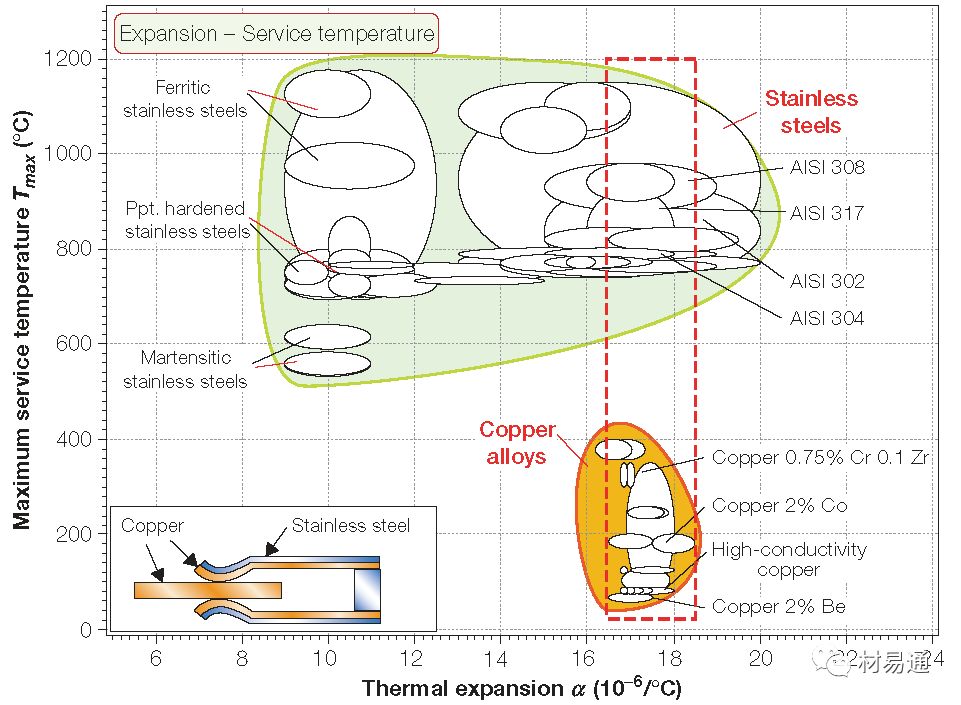
22
楊氏模量—自含能量
Young's Modulus vs. Energy
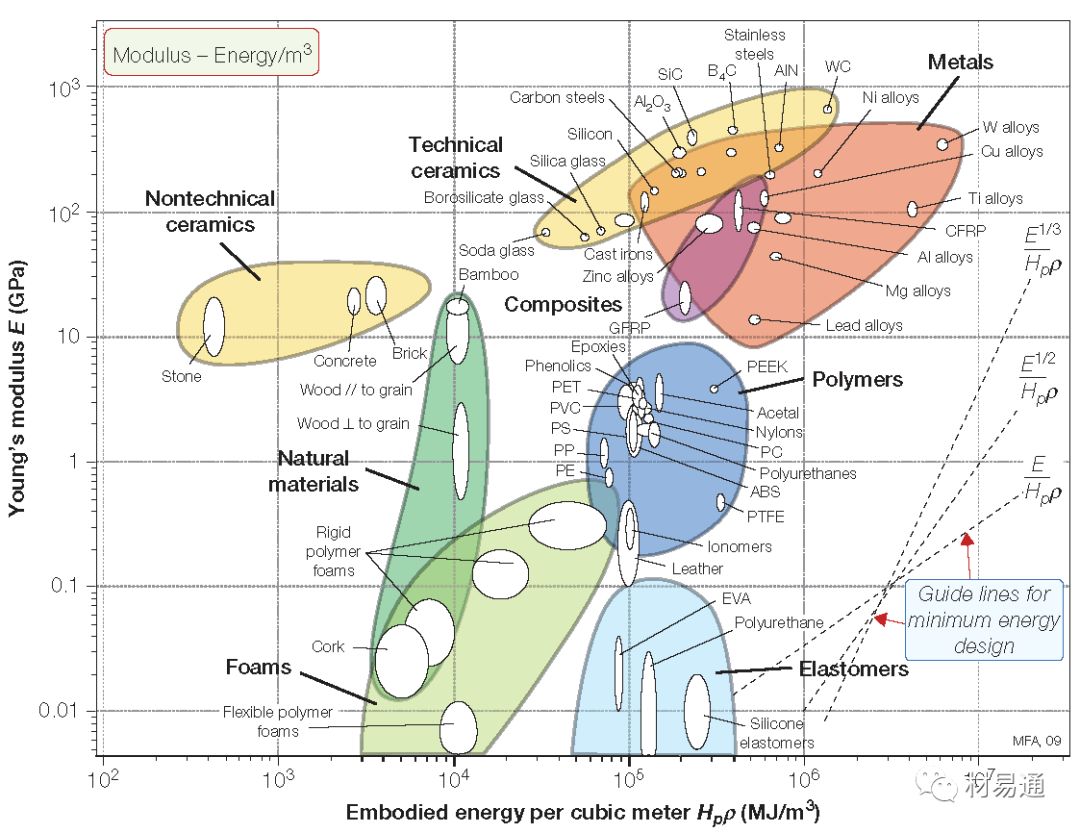
23
強度—自含能量
Strength vs. Energy
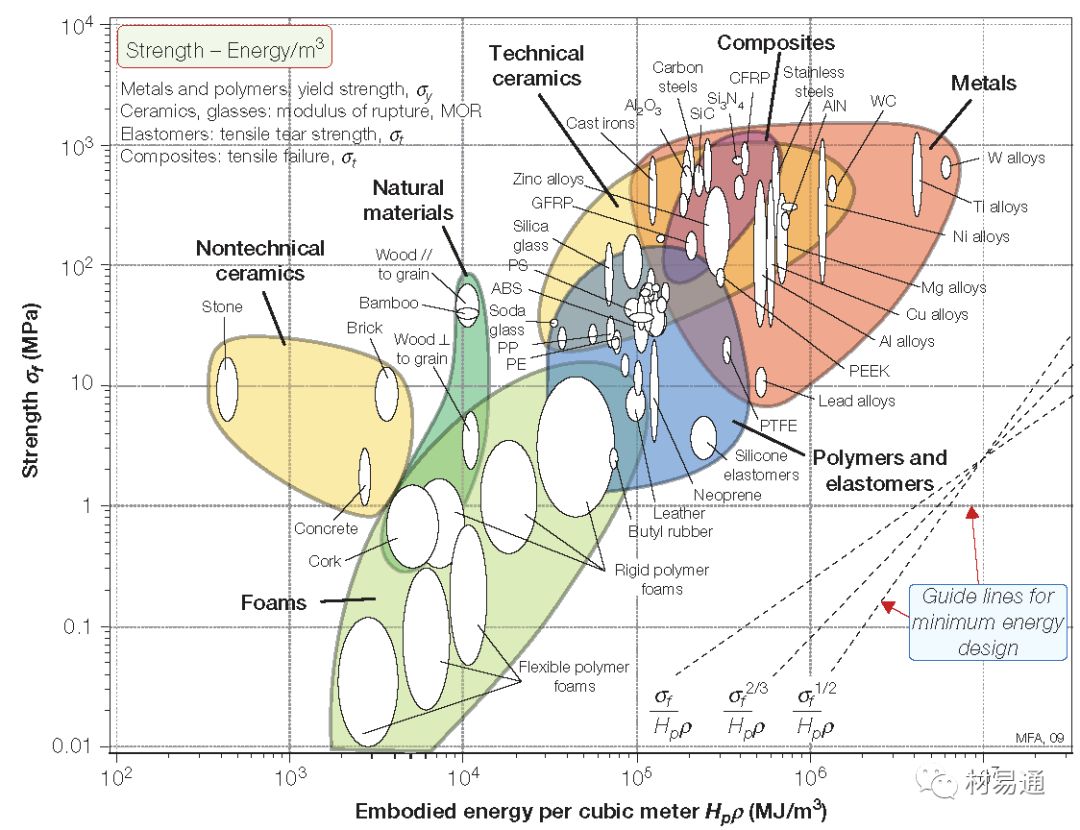
24
材料的觸覺性能(軟硬、暖涼)
Soft-Hard/Warm-Cold
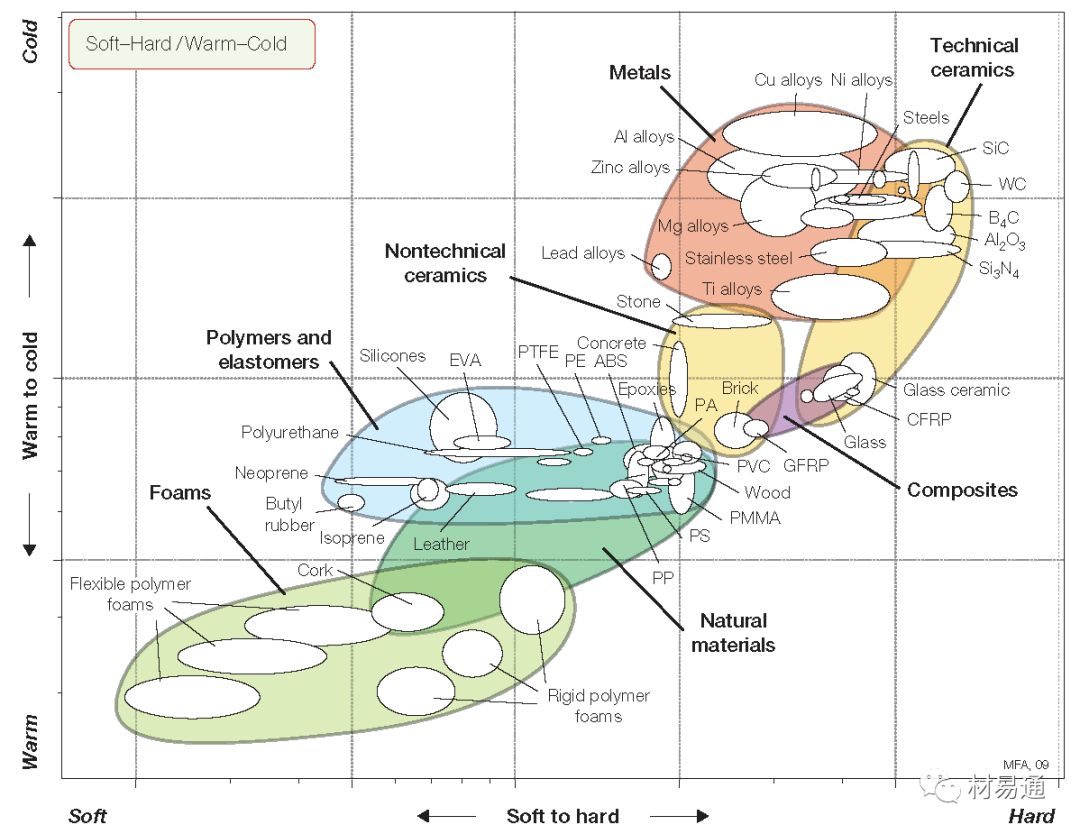
25
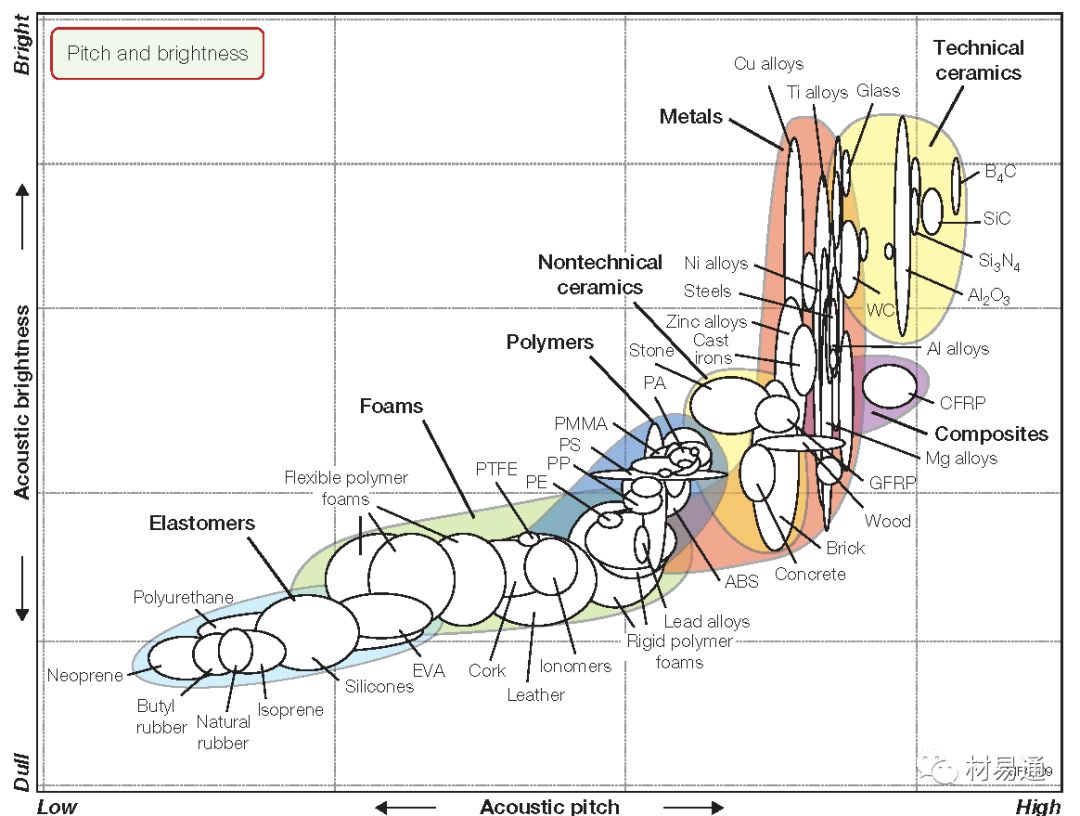
材料的音高與音色特性
Pitch and brightness
26
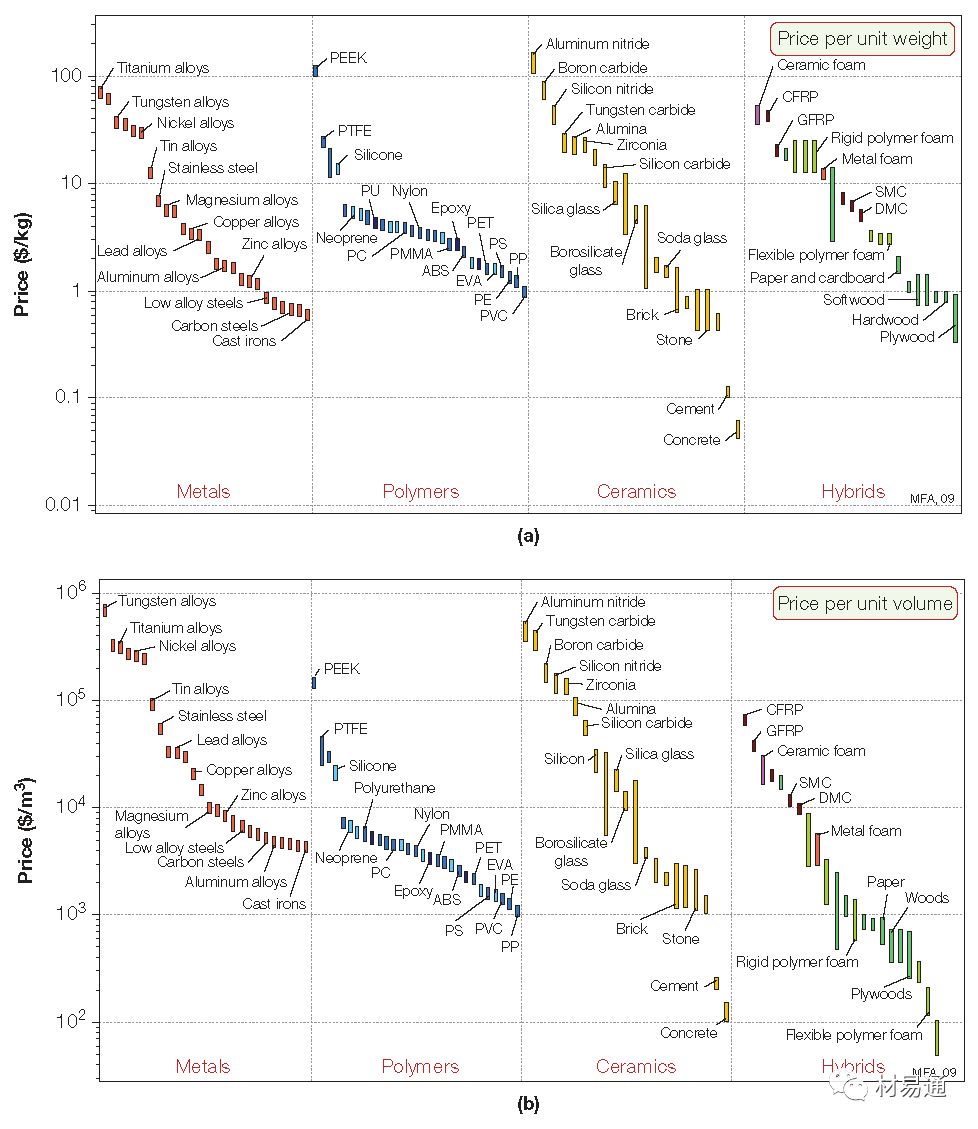
材料價格(單位重量或單位體積)
Price (unit weight & unit volume)
27
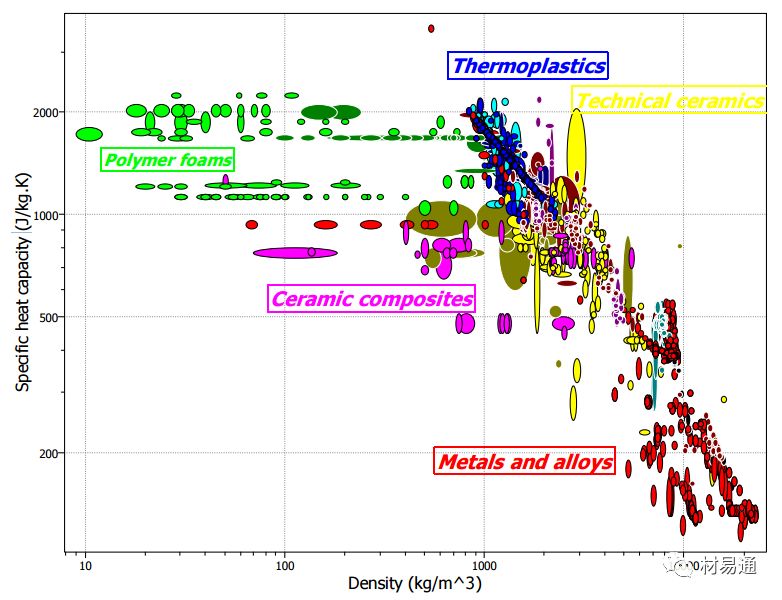
比熱容—密度
Specific Heat Capacity vs. Density
28
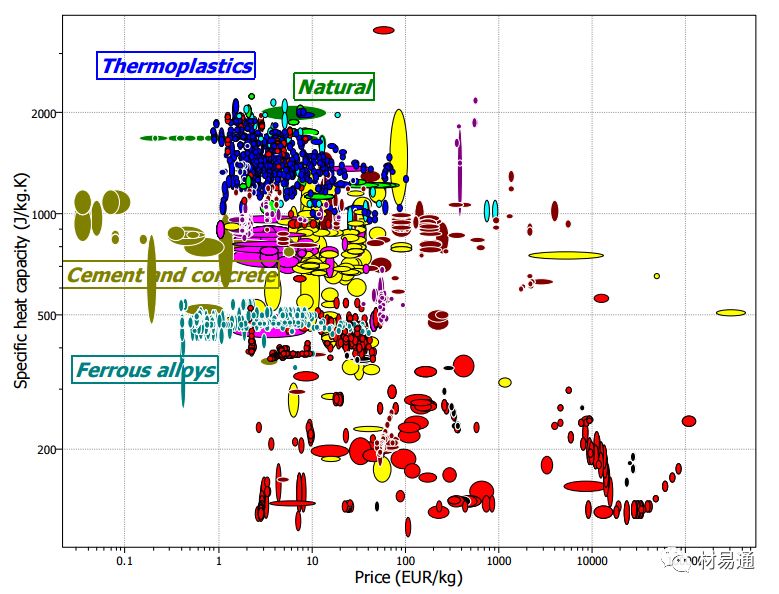
比熱容—價格
Specific Heat Capacity vs. Price
29
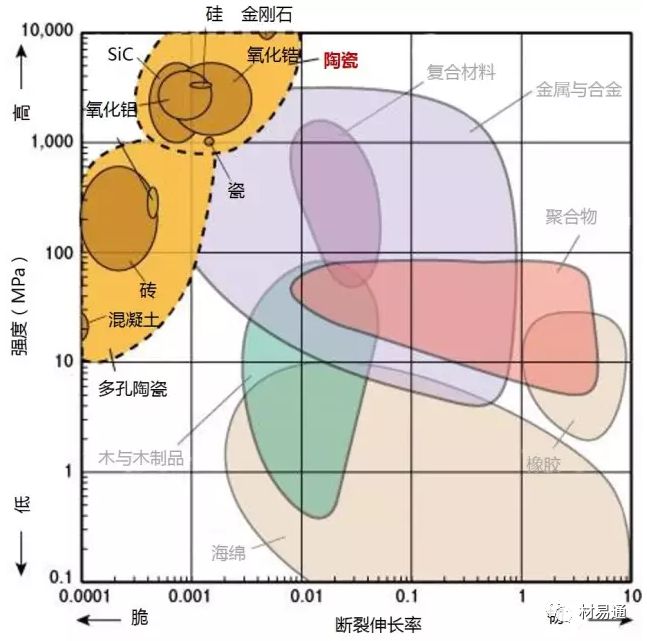
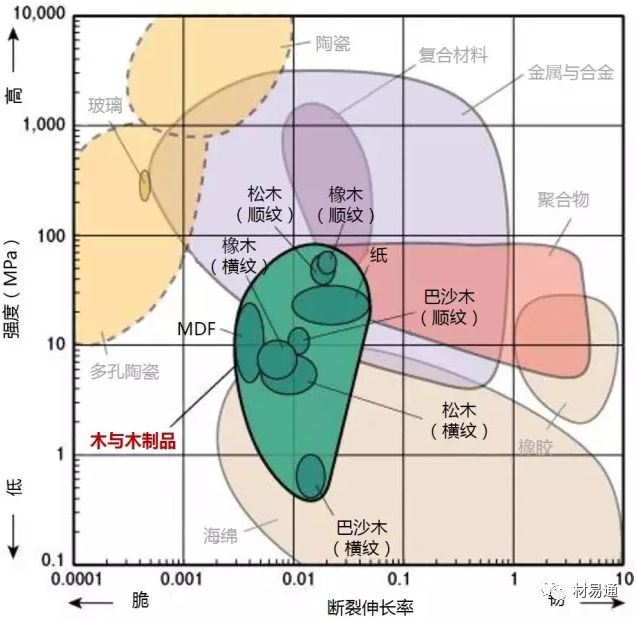
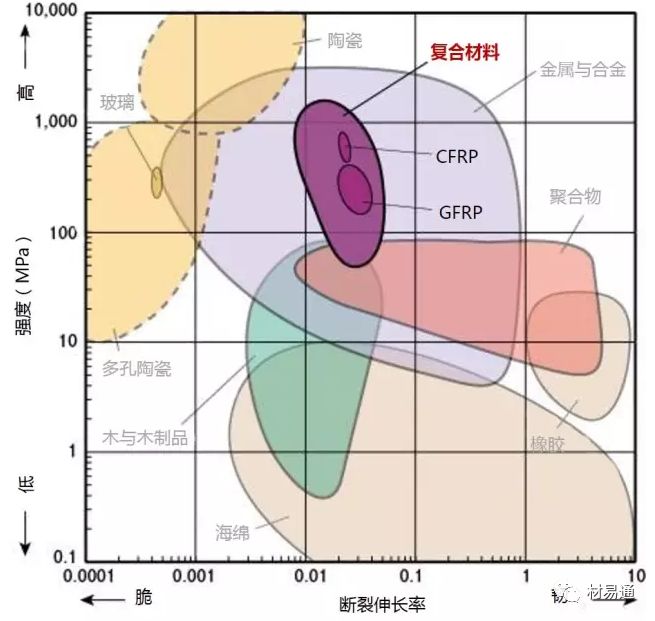
強度—延伸率
Strength vs. Elongation
30
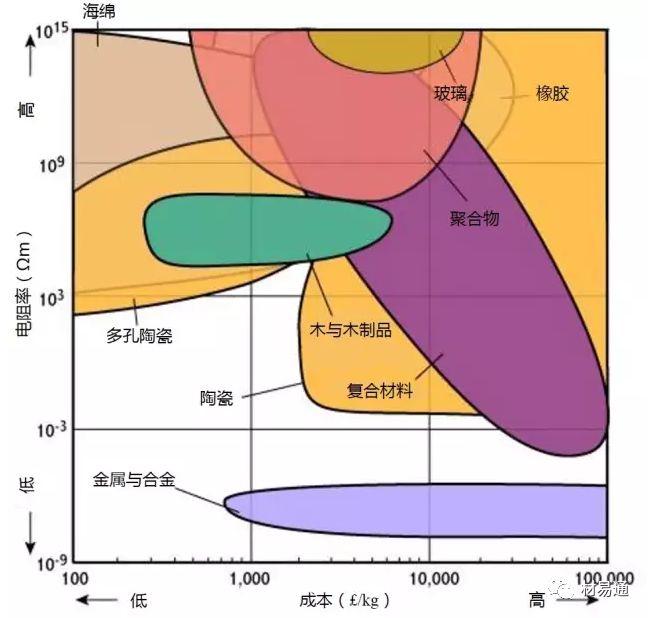
電阻率—成本
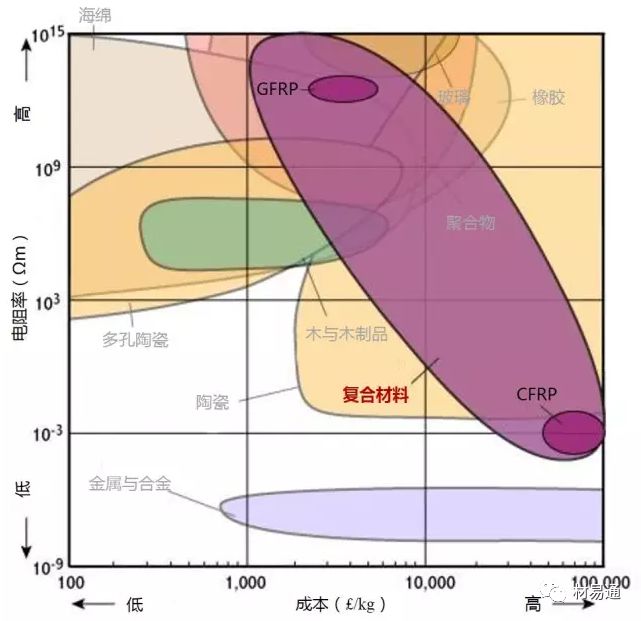
Electrical resistivity vs. Relative cost
31
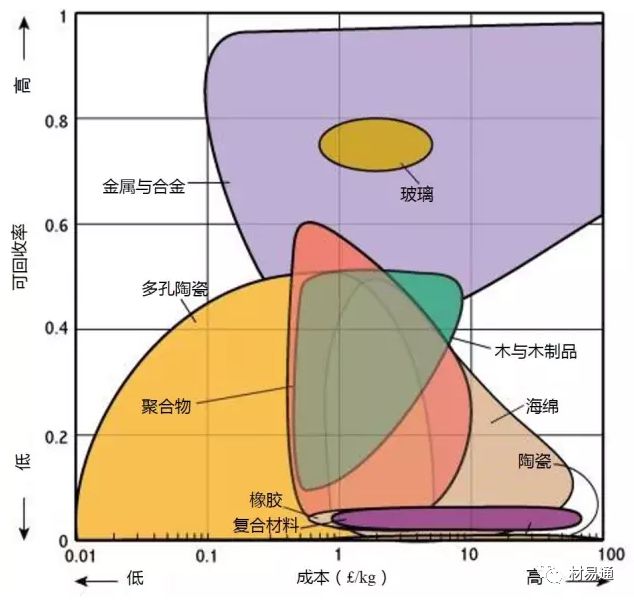
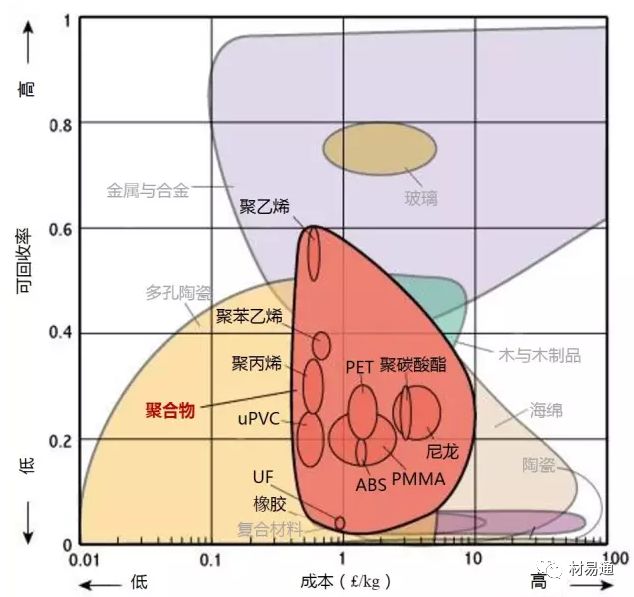
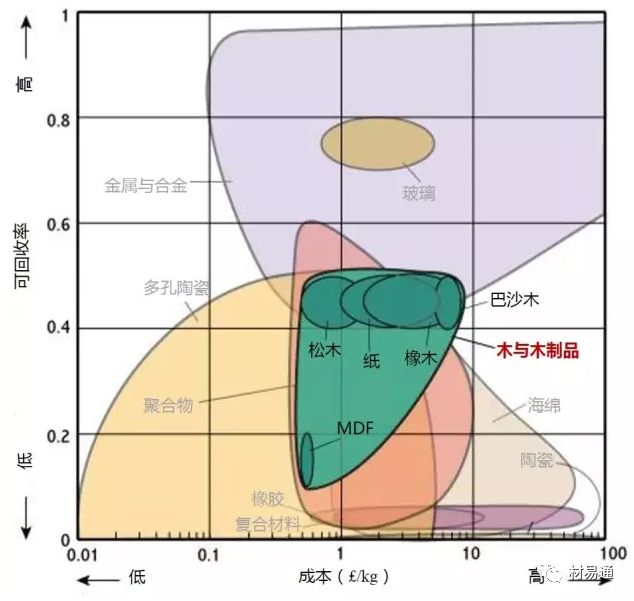
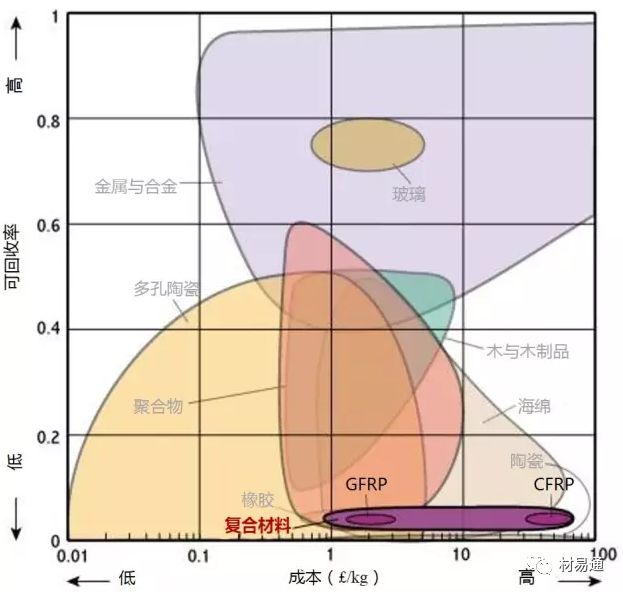
可回收率—成本
Recycle Fraction vs. Relative cost
32
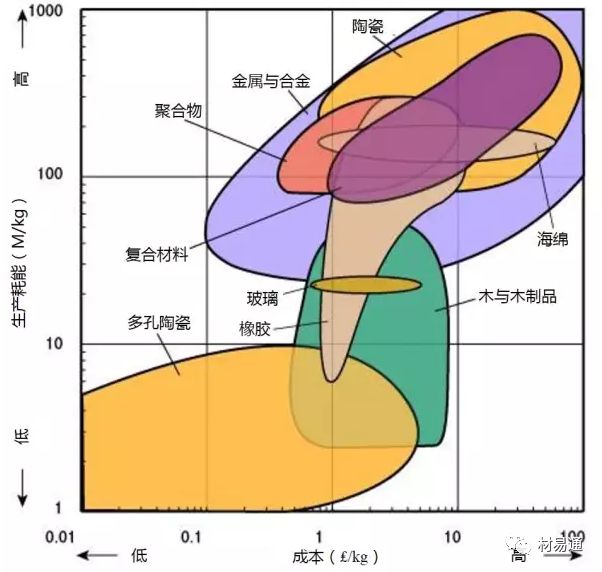
自含能量與成本
Embodied Energy vs. Relative Cost
完
參考來源:
1.《Materials Selection in Mechanical Design,Fourth Edition》;
2.新材料在線編譯內(nèi)容來源:http://www-materials.eng.cam.ac.uk/mpsite/interactive_charts/
PS:《Materials Selection in Mechanical Design,5th dition》的鏈接地址(能下的給小編傳一份啊):
https://www.elsevier.com/books/materials-selection-in-mechanical-design/ashby/978-0-08-100599-6

| |
|
? 請關(guān)注 微信公眾號: steeltuber. 轉(zhuǎn)載請保留鏈接: http://m.youwin2019.com/Steel-Knowledge/1616049552.html
|